hip labral tear special test|how can one heal a hip labral tear : specialty store The acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See more We have repaired just about every autoclave on the market, and continue to repair them everyday. Our guidance is based on that experience. Our Troubleshooting Guides & Technical Support is the best you can get .Browse 399 authentic autoclave stock photos, high-res images, and pictures, or explore additional dental autoclave or industrial autoclave stock images to find the right photo at the right size and resolution for your project.
{plog:ftitle_list}
- Traitement autoclave classe 4 : utilisation en contact avec le sol, avec stagnation d'eau possible - Face striée pour une meilleure résistance à la glissance - Certifié PEFC : bois issu d'une gestion forestière durable
labral tear physical exam tests
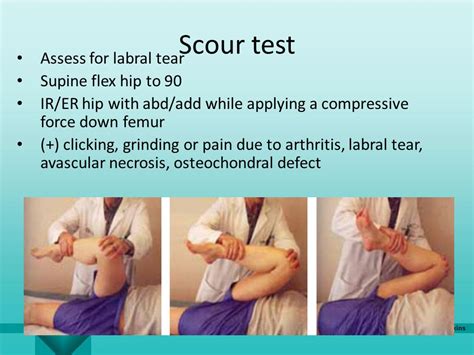
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See moreThe acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See moreStep 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See more
The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The .The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear.
is graduated pipette more accurate than volumetric
The FADIR test, standing for flexion, adduction and internal rotation test, is designed to evaluate the piriformis, gluteal muscles and hip joint as a source of pain. The patient is typically supine but can be laying on their contralateral side.The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the .
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and adduction.Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems; Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated; Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptoms
To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms including when they began and which activities aggravate them. The physical exam will likely involve moving your leg, and especially your hip joint, into various positions to check for pain and evaluate your hip's range of motion. He or she might also watch you walk. A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear.
The FADIR test, standing for flexion, adduction and internal rotation test, is designed to evaluate the piriformis, gluteal muscles and hip joint as a source of pain. The patient is typically supine but can be laying on their contralateral side.The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the . A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and adduction.
Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems; Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated; Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptomsTo diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms including when they began and which activities aggravate them. The physical exam will likely involve moving your leg, and especially your hip joint, into various positions to check for pain and evaluate your hip's range of motion. He or she might also watch you walk.
A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
how can one heal a hip labral tear
hip labrum physical exam test
is graduated pipette qualitative
What is an autoclave & how does it compare to a pressure cooker? An autoclave is a pressure device that uses strong heat and high pressure to sterilize. Unlike a pressure cooker, it is not used for cooking.
hip labral tear special test|how can one heal a hip labral tear